INTRODUCTION TO PROGRAMMING Unit - 01
What is C Language?
C is a general-purpose computer
programming language.
C is also said to be structures
programming language or function oriented . programming
language
C is a High level programming
language.
C is a programming language developed
at AT & T’s Bell Laboratories of USA in 1972.
It was designed and written by a man named Dennis Ritchie. In the late
seventies C began to replace the more familiar languages of that time like PL/I,
ALGOL, etc
Why do we use C?
C language is used to create
applications or software
Initially, C was developed to create
an operating system called UNIX.
The popular software like Linux OS,
PHP & MySQL are created using C language.
Why do we use C?
Generally C Language is used to
create the following…
·
Operating
Systems
·
Language
Compilers
·
Assemblers
·
Interpreters
·
Text
Editors
·
Network
Drivers
· Databases
History of C Language?
C Language was developed by Dennis Ritchie in the year of
1972
Born – September 9,
1941
Profession – Computer
Scientist
Place – Bell Labs, US
Known As – Father of C & UNIX
Awards – Turing Award(1983)
National
Medal of Technology(1998)
IEEE
Medal(1990)
Computer
Pioneer Award(1994)
Computer
History Museum Fellow(1997)
Harold
Pender Award(2003)
Died – October 12,
2011
·
Algorithms
An Algorithm is
step-by-step method of solving a problem . It is commonly used for data
processing calculation and other related computer and mathematical operation.
An algorithm is a set
of instruction design to perform spacify task. This can be simple process that
multiplying two numbers .
Charactistic of Algorithm-
Input
– The operation algorithm:- algorithm receives zero or more inputes
· Output- the Algorithm must produce at least one output.
· Finiteness – An Algorithm must terminate infinite amount of time .
· Effectiveness – each step in algorithm should be simple and very basic
· Definiteness – Every step in algorithm most be unambiguous.
Representation of
Algorithm
1)
As a Program
2)
As a Flow chart
3)
As a Pseudo Code
Ex of Algorithm—
Step 1- Start
Step 2 –Input /radius of circle
Step 3 – Area=^*r*r
Step 4- print Area
Step 5 – Stop.
· Flow-charts –
A flow chart is a pictorial
representation as an algorithm .It can be defined as a sequence of diagrammatic
representation of an algorithm.
A flowchart is a type of diagram that
represents a workflow or process. A flowchart can also be defined as a
diagrammatic representation of an algorithm, a step-by-step approach to solving
a task.
NEED OF FLOW CHART SYMBOLS :-
A flow chart uses boxes of different
types shapes to denote different type of instruction .The use of symbols having
standardized meaning makes it easier to communicate program logic through flow
chart . This is because use to standard symbol in a flow chart enables anyone
using the flow chart to interpret the logic easily .
(vi) Connectors :-
When the flow
chart spreads over more than one page it is useful to utilize connector symbol
as a substitute for flow lines
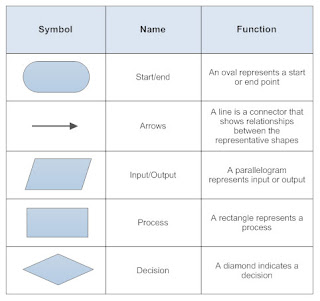
Basic
Flow Chart Symbols –
The basic flow chart symbols standardize by
the American National Standards Institute [ANSI] . Their function are describe
below –
Basic Symbol of flow chart -
(i) Terminal / Start :- It is the first and the last symbol in flow
chart.
(ii) Input / Output :-
They also
indicates instruction to input / output
data
from / to a storage device
(iii) Processing :- A processing
symbol represents arithmetic and data movement instruction . It is indicate all
arithmetic process of adding , subtraction , multiplying and dividing . They also indicates
logical proves of moving data from one memory location to another
Note:- Processing [ used when there in assignment
operator (=) or arithmetic operator ( + , - , * , /).
(iv) Decision :- A decision symbol
indicates a decision point , which is a point at which a branch to one of two
or more alternative path is possible . A decision symbol also accounts for all
possible exit path depending on the result of decision .
(v) Flow Lines :-
In flow chart ,
use of flow lines with arrow heads indicates flow of operation , normal flow of
flow chart is from top-to-bottom and left-to-right

·
Programming Languages
Program :- Program is a set of instruction which
is written in sequence manners using syntax of any programming language.
Programming Language - Computer language or
programming language is a language acceptable to computer system and the
process of writing instruction in such a language is called programming or coding.
Types of programming language –
Low level language –
1.
Machine Language –This
is the 1st generation language and computer works this language .
This is also known as Low level language here all instruction where given is
binary form and is transferd to machine language . It is very difficult for
write or read instruction written in binary form
2.
Assembly
language
– This is the 2nd generation language . The symbolic instruction
language is called assembly . To execute these instruction all mnemonics are
help of translator known as Assembler
High- level language –
This is the 3rd
generation language .In this language instruction are written using English language with symbol and digits . It is Machine in depended language .
·
Linking and Loading
Linking-
Linking
is the process of collecting and combining various piecas of code and data into
a single file that can be loaded into memory and executed
Loader
– The
job of loader is to load the program from secondry memory to main memory for
execution
Static
Loader – Load the program from secondary to main memory before the
compileson
Linking and Loading are
the utility programs that play a important role in the execution of a program.
Linking intakes the object codes generated by the assembler and combines them
to generate the executable module. On the other hand, the loading loads this
executable module to the main memory for execution.
Loading:
Bringing the program from secondary memory to main memory is called Loading.
Bringing the program from secondary memory to main memory is called Loading.
Linking:
Establishing the linking between all the modules or all the functions of the program in order to continue the program execution is called linking.
Establishing the linking between all the modules or all the functions of the program in order to continue the program execution is called linking.
Differences between Linking and
Loading:
1.
The key
difference between linking and loading is that the linking generates the
executable file of a program whereas, the loading loads the executable file
obtained from the linking into main memory for execution.
2.
The
linking intakes the object module of a program generated by the assembler.
However, the loading intakes the executable module generated by the linking.
3.
The
linking combines all object modules of a program to generate executable modules
it also links the library function in the object module to built-in libraries
of the high-level programming language. On the other hand, loading allocates
space to an executable module in main memory.
·
Testing and Debugging
Testing
:-
(i) It is the process to find error
(ii) Testing can be manual or automated
(iii) Testing is done by tester
(iv) Testing is display of error
Debugging
:-
(i) It is the process to correct the error
find debugging testing
(ii) Debugging is always manual .It can not be automated
(iii) Debugging is done by programmer or developer
(iv) Debugging is deducting process
· Documentation –
While writing programs it is a good
programming practice to make a brief explanatory segments . This explanatory
note is called a comment .It explain how to program works and
how to interact with it Thus it helps other programmers to understand the
program.
There are two types of documentation
(i) Internal Documentation :- This documentation is a comment
statement within a program .It describe the function of the program pr program
segment . these statement are not translated to machine language .
(ii) External Documentation :- This
documentation is an executable statement in a program . It may be message to
the user to respond to the program requirement
· Programming Style-Names:-
Programming style also known as
Code Style. It is set of rules pr guidelines used when writing the source code
for a program by following a particular programming style will hop programming
style to read & understand source code & help to a void corroding
errors.


No comments:
Post a Comment