Introduction to Arrays
An array is a collection of homogeneous (same type) data items stored in contiguous memory locations. For example if an array is of type “int”, it can only store integer elements and cannot allow the elements of other types such as double, float, char etc.
An array is collection of items stored at contiguous memory locations. The idea is to store multiple items of same type together. This makes it easier to calculate the position of each element by simply adding an offset to a base value, i.e., the memory location of the first element of the array (generally denoted by the name of the array).
Why we need an array?
Array is particularly useful when we are dealing with lot of variables of the same type. For example, lets say I need to store the marks in math subject of 100 students. To solve this particular problem, either I have to create the 100 variables of int type or create an array of int type with the size 100.
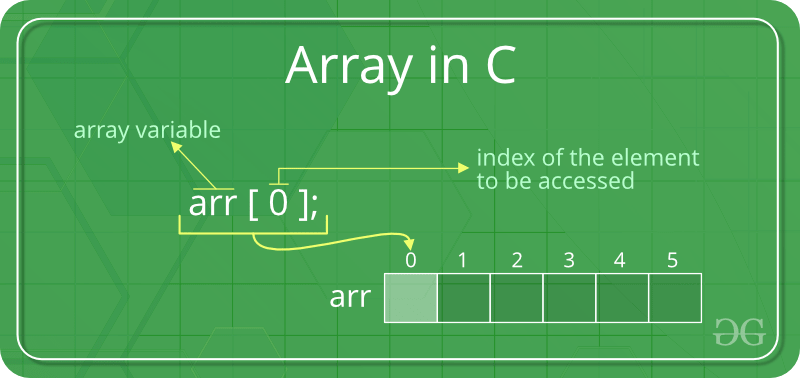
Array Representation
Arrays can be declared in various ways in different languages. For illustration, let's take C array declaration.

Arrays can be declared in various ways in different languages. For illustration, let's take C array declaration.

As per the above illustration, following are the important points to be considered.
- Index starts with 0.
- Array length is 10 which means it can store 10 elements.
- Each element can be accessed via its index. For example, we can fetch an element at index 6 as 9.
Types of Arrays in C
In c programming language, arrays are classified into two types. They are as follows...
- Single Dimensional Array / One Dimensional Array
- Multi Dimensional Array
Single Dimensional Array
In c programming language, single dimensional arrays are used to store list of values of same datatype.
In other words, single dimensional arrays are used to store a row of values. In single dimensional array,
data is stored in linear form. Single dimensional arrays are also called as one-dimensional arrays,
Linear Arrays or simply 1-D Arrays.
Declaration of Single Dimensional Array
We use the following general syntax for declaring a single dimensional array...
datatype arrayName [ size ] ;
Example Code
int rollNumbers [60] ;
The above declaration of single dimensional array reserves 60 continuous memory locations of 2 bytes each with the name rollNumbers and tells the compiler to allow only integer values into those memory locations.
Initialization of Single Dimensional Array
We use the following general syntax for declaring and initializing a single dimensional array with size and initial values.
datatype arrayName [ size ] = {value1, value2, ...} ;
Example Code
int marks [6] = { 89, 90, 76, 78, 98, 86 } ;
The above declaration of single dimensional array reserves 6 contiguous memory locations of 2 bytes each with the name marks and initializes with value 89 in first memory location, 90 in second memory location, 76 in third memory location, 78 in fourth memory location, 98 in fifth memory location and 86 in sixth memory location.
We can also use the following general syntax to intialize a single dimensional array without specifying size and with initial values..
datatype arrayName [ ] = {value1, value2, ...} ;
The array must be initialized if it is created without specifying any size. In this case, the size of the array is decided based on the number of values initialized.
int marks [6] = { 89, 90, 76, 78, 98, 86 } ;
Example Code
int marks [] = { 89, 90, 76, 78, 98, 86 } ;
char studentName [] = "btechsmartclass" ;
int marks [] = { 89, 90, 76, 78, 98, 86 } ;
char studentName [] = "btechsmartclass" ;
In the above example declaration, size of the array 'marks' is 6 and the size of the array 'studentName' is 16. This is because in case of character array, compiler stores one exttra character called \0 (NULL) at the end.
Accessing Elements of Single Dimensional Array
In c programming language, to access the elements of single dimensional array we use array name followed by index value of the element that to be accessed. Here the index value must be enclosed in square braces. Index value of an element in an array is the reference number given to each element at the time of memory allocation. The index value of single dimensional array starts with zero (0) for first element and incremented by one for each element. The index value in an array is also called as subscript or indices.
We use the following general syntax to access individual elements of single dimensional array...
arrayName [ indexValue ]
We use the following general syntax to access individual elements of single dimensional array...
arrayName [ indexValue ]
Example Code
marks [2] = 99 ;
In the above statement, the third element of 'marks' array is assinged with value '99'.
marks [2] = 99 ;
Multi Dimensional Array
An array of arrays is called as multi dimensional array. In simple words, an array created with more than one dimension (size) is called as multi dimensional array. Multi dimensional array can be of two dimensional array or three dimensional array or four dimensional array or more...
Most popular and commonly used multi dimensional array is two dimensional array. The 2-D arrays are used to store data in the form of table. We also use 2-D arrays to create mathematical matrices.
Declaration of Two Dimensional Array
We use the following general syntax for declaring a two dimensional array...
datatype arrayName [ rowSize ] [ columnSize ] ;
Most popular and commonly used multi dimensional array is two dimensional array. The 2-D arrays are used to store data in the form of table. We also use 2-D arrays to create mathematical matrices.
datatype arrayName [ rowSize ] [ columnSize ] ;
Example Code
int matrix_A [2][3] ;
The above declaration of two dimensional array reserves 6 continuous memory locations of 2 bytes each in the form of 2 rows and 3 columns.
Initialization of Two Dimensional Array
We use the following general syntax for declaring and initializing a two dimensional array with specific number of rows and coloumns with initial values.
datatype arrayName [rows][colmns] = {{r1c1value, r1c2value, ...},{r2c1, r2c2,...}...} ;
int matrix_A [2][3] ;
datatype arrayName [rows][colmns] = {{r1c1value, r1c2value, ...},{r2c1, r2c2,...}...} ;
Example Code
int matrix_A [2][3] = { {1, 2, 3},{4, 5, 6} } ;
The above declaration of two-dimensional array reserves 6 contiguous memory locations of 2 bytes each in the form of 2 rows and 3 columns. And the first row is initialized with values 1, 2 & 3 and second row is initialized with values 4, 5 & 6.
We can also initialize as follows...
int matrix_A [2][3] = { {1, 2, 3},{4, 5, 6} } ;
Example Code
int matrix_A [2][3] = {
{1, 2, 3},
{4, 5, 6}
} ;
Accessing Individual Elements of Two Dimensional Array
In a c programming language, to access elements of a two-dimensional array we use array name followed by row index value and column index value of the element that to be accessed. Here the row and column index values must be enclosed in separate square braces. In case of the two-dimensional array the compiler assigns separate index values for rows and columns.
We use the following general syntax to access the individual elements of a two-dimensional array...
arrayName [ rowIndex ] [ columnIndex ]
int matrix_A [2][3] = {
{1, 2, 3},
{4, 5, 6}
} ;
We use the following general syntax to access the individual elements of a two-dimensional array...
arrayName [ rowIndex ] [ columnIndex ]
Example Code
matrix_A [0][1] = 10 ;
In the above statement, the element with row index 0 and column index 1 of matrix_A array is assinged with value 10.
Basic Operations
matrix_A [0][1] = 10 ;
Basic Operations
Following are the basic operations supported by an array.
- Traverse − print all the array elements one by one.
- Insertion − Adds an element at the given index.
- Deletion − Deletes an element at the given index.
- Search − Searches an element using the given index or by the value.
- Update − Updates an element at the given index.
Types of indexing in array:
- 0 (zero-based indexing): The first element of the array is indexed by subscript of 0
- 1 (one-based indexing): The second element of the array is indexed by subscript of 1
- n (n-based indexing): The base index of an array can be freely chosen. Usually programming languages allowing n-based indexing also allow negative index values and other scalar data types like enumerations, or characters may be used as an array index.
Advantages of using arrays:
- Arrays allow random access of elements. This makes accessing elements by position faster.
- Arrays have better cache locality that can make a pretty big difference in performance.
Disadvantages
1. While using array, we must need to make the decision of the size of the array in the beginning, so if we are not aware how many elements we are going to store in array, it would make the task difficult.
2. The size of the array is fixed so if at later point, if we need to store more elements in it then it can’t be done. On the other hand, if we store less number of elements than the declared size, the remaining allocated memory is wasted
Example
Following program traverses and prints the elements of an array:
#includemain() { int LA[] = {1,3,5,7,8}; int item = 10, k = 3, n = 5; int i = 0, j = n; printf("The original array elements are :\n"); for(i = 0; i Output
The original array elements are : LA[0] = 1 LA[1] = 3 LA[2] = 5 LA[3] = 7 LA[4] = 8Time complexity of Array
Lets take a look at the time complexity of various operations on arrays.
Operation Average Case Worst Case Read O(1) O(1) Insert O(n) O(n) Delete O(n) O(n) Search O(n) O(n) Applications of Arrays in C
In c programming language, arrays are used in wide range of applications. Few of them are as follows...● Arrays are used to Store List of valuesIn c programming language, single dimensional arrays are used to store list of values of same datatype.In other words, single dimensional arrays are used to store a row of values. In single dimensional array data is stored in linear form.● Arrays are used to Perform Matrix OperationsWe use two dimensional arrays to create matrix. We can perform various operations on matrices using two dimensional arrays.● Arrays are used to implement Search AlgorithmsWe use single dimensional arrays to implement search algorihtms like ...● Arrays are used to implement Sorting AlgorithmsWe use single dimensional arrays to implement sorting algorihtms like ...
- Insertion Sort
- Bubble Sort
- Selection Sort
- Quick Sort
- Merge Sort, etc.,
● Arrays are used to implement DatastructuresWe use single dimensional arrays to implement datastructures like...

No comments:
Post a Comment